Медаль Хьюза

Multi tool use
| Медаль Хьюза | |
|---|---|
| Оригинальное название | англ. Hughes Medal |
| Страна | |
| Тип | медаль |
| Кем вручается | Лондонское королевское общество |
| Статус | вручается |
| Статистика | |
| Дата учреждения | 1902 год |
| Первое награждение | 1902 год |
| Количество награждений | 107 |
| Сайт | Медаль Хьюза |
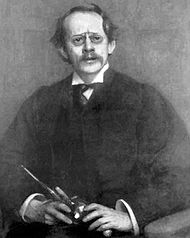
Джозеф Томсон первым получил медаль Хьюза в 1902 году «за большой вклад в науку об электричестве»
Медаль Хьюза (англ. Hughes Medal) — награда Лондонского королевского общества, присуждаемая «за оригинальные открытия в области физических наук, особенно связанных с производством, хранением и использованием энергии». Учреждена в честь изобретателя Дэвида Хьюза[1]. С 2011 года вручается раз в два года.
Впервые медаль была вручена в 1902 году, её получил Джозеф Томсон «за большой вклад в науку об электричестве». С тех пор она вручалась ежегодно, лишь в 1924 и 2009 годах по неизвестной причине никто не был удостоен медали. В отличие от других наград Лондонского королевского общества, медаль Хьюза никогда не присуждалась дважды одному и тому же лауреату[1].
Бывали случаи, когда медаль присуждалась одновременно нескольким учёным: в 1938 году Джону Кокрофту и Эрнесту Уолтону, в 1981 году Питеру Хиггсу и Тому Кибблу, в 1982 году её получили Драммонд Мэтьюз и Фредерик Вайн, а в 1988 году Арчибальд Хоуи и М. Уилан[1].
Награда присуждается гражданам стран Содружества наций и Ирландии, или же работающим в них не менее трёх лет иностранным учёным. Медаль выполнена из серебра с позолотой и сопровождается денежной премией в размере 2000 фунтов[1].
Медалью награждены 30 лауреатов Нобелевской премии.
Награждённые медалью Хьюза |
| Год |
Имя |
Обоснование |
|---|---|---|
| 1902 | "For his numerous contributions to electric science, especially in reference to the phenomena of electric discharge in gases" |
|
| 1903 | Иоганн Вильгельм Гитторф | "For his long continued experimental researches on the electric discharge in liquids and gases" |
| 1904 | Джозеф Уилсон Суон | "For his invention of the incandescent lamp, and his other inventions and improvements in the practical applications of electricity" |
| 1905 | Аугусто Риги | "For his experimental researches in electrical science, including electric vibrations" |
| 1906 | Герта Маркс Айртон | "For her experimental investigations on the electric arc, and also on sand ripples" |
| 1907 | Эрнест Говард Гриффитс[en] | "For his contributions to exact physical measurement" |
| 1908 | Ойген Гольдштейн | "For his discoveries on the nature of electric discharge in rarefied gasses" |
| 1909 | Ричард Глейзбрук | "For his researches on electrical standards" |
| 1910 | Флеминг Джон Амброз | "For his researches in electricity and electrical measurements" |
| 1911 | "For his work on nuclei in dust-free air, and his work on ions in gases and atmospheric electricity" |
|
| 1912 | Уильям Дадделл[en] | "For his investigations in technical electricity" |
| 1913 | Александер Грэм Белл | "For his share in the invention of the telephone, and more especially the construction of the telephone receiver" |
| 1914 | Джон Сили Таунсенд | "For his researches on electric induction in gases" |
| 1915 | Поль Ланжевен | "For his important contributions to, and pre-eminent position in, electrical science" |
| 1916 | Элиу Томсон | "For his researches in experimental electricity" |
| 1917 | "For his researches in connexion with X-ray radiation" |
|
| 1918 | "For his researches in molecular physics" |
|
| 1919 | Чарльз Чри[en] | "For his researches in terrestrial magnetism" |
| 1920 | "For his work in experimental physics, and especially thermionics" |
|
| 1921 | "For his research in theoretical physics" |
|
| 1922 | "For his discovery of isotopes of a large number of the elements by the method of positive rays" |
|
| 1923 | "For his determination of the electronic charge and of other physical constants" |
|
| 1924 | Не вручалась |
|
| 1925 | Фрэнк Эдвард Смит[en] | "For his determination of fundamental electrical units and for researches in technical electricity" |
| 1926 | Генри Джексон[en] | "For his pioneer work in the scientific investigations of radiotelegraphy and its application to navigation" |
| 1927 | Уильям Кулидж[en] | "For his work on the X-rays and the development of highly efficient apparatus for their production" |
| 1928 | Морис де Бройль | "For his work on X-ray spectra" |
| 1929 | Ханс Вильгельм Гейгер | "For his invention and development of methods of counting alpha and beta particles" |
| 1930 | "For his studies on the abnormal scattering of light" |
|
| 1931 | "For his pioneer work on the elucidation of crystal structure by X-ray analysis" |
|
| 1932 | "For his researches on radioactivity" |
|
| 1933 | "For his researches into the effect of the Heaviside layer upon the transmission of wireless signals" |
|
| 1934 | "For his work as a physicist and technician on long-wave X-rays" |
|
| 1935 | "For his research that resulted in the discovery of the physical existence of electron waves through long-continued investigations on the reflection of electrons from the crystal planes of nickel and other metals" |
|
| 1936 | Вальтер Шоттки | "For his discovery of the Schrot Effect in thermionic emission and his invention of the screen-grid tetrode and a superheterodyne method of receiving wireless signals" |
| 1937 | "For his work on the development of the cyclotron and its application to investigations of nuclear disintegration" |
|
| 1938 | "For their discovery that nuclei could be disintegrated by artificially produced bombarding particles" |
|
| 1939 | "For his important discoveries in connexion with the diffraction of electrons by matter" |
|
| 1940 | "For his discovery of the Compton Effect; and for his work on cosmic rays" |
|
| 1941 | "For his fertile application of the principles of quantum theory to many branches of physics, especially in the fields of nuclear and collision theory, in the theory of metals and in the theory of photographic emulsions" |
|
| 1942 | "For his outstanding contributions to the knowledge of the electrical structure of matter, his work in quantum theory, and his experimental studies of the neutron" |
|
| 1943 | Марк Олифант | "For his distinguished work in nuclear physics and mastery of methods of generating and applying high potentials" |
| 1944 | Джордж Финч[en] | "For his fundamental contributions to the study of the structure and properties of surfaces, and for his important work on the electrical ignition of gases" |
| 1945 | Базиль Шонленд[en] | "For his work on atmospheric electricity and of other physical researches" |
| 1946 | Джон Рэндалл | "For his distinguished researches into fluorescent materials and into the production of high frequency electro-magnetic radiation" |
| 1947 | "For his distinguished contributions to nuclear physics, particularly the discovery of artificial radioactivity and of neutron emission in the fission process" |
|
| 1948 | Роберт Уотсон-Уотт | "For his distinguished contributions to atmospheric physics and to the development of radar" |
| 1949 | "For his distinguished work on the photography of particle tracks, and in connexion with the discovery of mesons and their transformation" |
|
| 1950 | "For his contributions to theoretical physics in general and to the development of quantum mechanics in particular" |
|
| 1951 | Хендрик Антони Крамерс | "For his distinguished work on the quantum theory, particularly its application to the optical and magnetic properties of matter" |
| 1952 | Филипп Ди[en] | "particularly for his distinguished studies on the disintegration of atomic nuclei, particularly those using the Wilson cloud chamber technique" |
| 1953 | Эдвард Баллард[en] | "For his important contributions to the development, both theoretical and experimental, of the physics of the Earth" |
| 1954 | "For his distinguished and original experimental researches in radio astronomy" |
|
| 1955 | Гарри Стюарт Мэсси | "For his distinguished contributions to atomic and molecular physics, particularly in regard to collisions involving the production and recombination of ions" |
| 1956 | Фредерик Линдеманн[en] | "For his distinguished work in many fields: the melting point formula and theory of specific heats; ionisation of stars; meteors and temperature inversion in the stratosphere" |
| 1957 | Джозеф Праудмен[en] | "For his distinguished work on dynamical oceanography" |
| 1958 | Эдвард Андраде[en] | "For his distinguished contributions to many branches of classical physics" |
| 1959 | Брайан Пиппард[en] | "For his distinguished contributions in the field of low temperature physics" |
| 1960 | Джозеф Лейд Пози | "For his distinguished contributions to radio astronomy both in the study of solar and of cosmic ray emission" |
| 1961 | Алан Коттрелл | "For his distinguished work on the physical properties of metals, particularly in relation to mechanical deformation and to the effects of irradiation" |
| 1962 | Бребис Блини | "For his distinguished studies of electrical and magnetic phenomena and their correlation with atomic and molecular properties" |
| 1963 | Фредерик Калланд Уильямс[en] | "For distinguished work on early computers" |
| 1964 | "For his distinguished contributions to quantum mechanics and the theory of fundamental particles" |
|
| 1965 | Дэнис Уилкинсон[en] | "For his distinguished experimental and theoretical investigation in nuclear structure and high energy physics" |
| 1966 | Николас Кеммер | "For his numerous discoveries of major importance in theoretical nuclear physics which he has made" |
| 1967 | Курт Мендельсон | "For his distinguished contributions to cryophysics, especially his discoveries in superconductivity and superfluidity" |
| 1968 | Фримен Дайсон | "For his distinguished fundamental work in theoretical physics, and especially on quantum electrodynamics" |
| 1969 | Николас Курти | "For his distinguished work in low-temperature physics and in thermodynamics" |
| 1970 | Дэвид Бейтс[en] | "For his distinguished contributions to theoretical atomic and molecular physics and its applications to atmospheric physics, plasma physics and astrophysics" |
| 1971 | Роберт Хэнбери Браун | "For his distinguished work in developing a new form of stellar interfrometer [sic], culminating in his observations of alpha virginis" |
| 1972 | "Particularly for his discovery of the remarkable properties of junctions between superconducting materials" |
|
| 1973 | Питер Хирш | "For his distinguished contributions to the development of the electron microscope thin film technique for the study of crystal defects and its application to a very wide range of problems in materials science and metallurgy" |
| 1974 | Питер Фоулер[en] | "For his outstanding contributions to cosmic ray and elementary particle physics" |
| 1975 | Ричард Далитц[en] | "For his distinguished contributions to the theory of the basic particles of matter" |
| 1976 | Стивен Хокинг | "For his distinguished contributions to the application of general relativity to astrophysics, especially to the behaviour of highly condensed matter" |
| 1977 | "For his outstanding contributions to radioastronomy, including the discovery and identification of pulsars" |
|
| 1978 | Уильям Кокрейн[en] | "For his pioneering contributions to the science of X-ray crystallography, in which his work has made a profound impact on its development and application, and for his original contributions to lattice dynamics and its relation to phase transitions, which stimulated a new and fruitful field of results" |
| 1979 | Роберт Джозеф Патон Уильямс[en] | "For his distinguished studies of the conformations of computer molecules in solution by the use of nuclear magnetic resonance" |
| 1980 | Фрэнсис Фарли[en] | "For his ultra-precise measurements of the muon magnetic moment, a severe test of quantum electrodynamics and of the nature of the muon" |
| 1981 | "For their international contributions about the spontaneous breaking of fundamental symmetries in elementary-particle theory" |
|
| 1982 | Драммонд Мэтьюз[en] и Фредерик Вайн[en] |
"For their elucidation of the magnetic properties of the ocean floors which subsequently led to the plate tectonic hypothesis" |
| 1983 | Джон Клайв Уорд | "For his highly influential and original contributions to quantum field theory, particularly the Ward identity and the Salam-Ward theory of weak interactions" |
| 1984 | Рой Керр | "For his distinguished work on relativity, especially for his discovery of the so-called Kerr Black Hole, which has been very influential" |
| 1985 | Тони Скирм[en] | "For his contributions to theoretical particle and nuclear physics, and his discovery that particle-like entities simulating the properties of baryons can occur in non-linear meson field theories" |
| 1986 | Майкл Вульфсон[en] | "For the creation of algorithms including MULTAN and SAYTAN which are used world-wide to solve the majority of reported crystal structures" |
| 1987 | Майкл Пеппер[en] | "For his many important experimental investigations into the fundamental properties of semiconductors especially low-dimensional systems, where he has elucidated some of their unusual properties like electron localization and the Quantum Hall effects" |
| 1988 | Арчибальд Хоуи[en] и M. Дж. Уилан[en] |
"For their contributions to the theory of electron diffraction and microscopy, and its application to the study of lattice defects in crystals" |
| 1989 | Джон Стюарт Белл | "For his outstanding contributions to our understanding of the structure and interpretation of quantum theory, in particular demonstrating the unique nature of its predictions" |
| 1990 | Томас Джордж Каулинг[en] | "For his fundamental contributions to theoretical astrophysics including seminal theoretical studies of the role of electromagnetic induction in cosmic systems" |
| 1991 | Филип Бартон Мун[en] | "For his contributions in three main areas of science — nuclear physics, the discovery of gamma-ray resonances, and the use of colliding molecular beams to study chemical reactions" |
| 1992 | Майкл Ситон[en] | "For his theoretical research in atomic physics and leadership of the Opacity Project" |
| 1993 | Джордж Исаак[en] | "For his pioneering use of resonant scattering techniques to make extremely precise measures of Doppler velocity shifts in the solar photosphere" |
| 1994 | Роберт Чемберс[en] | "For his many contributions to solid-state physics, in particular his ingenious and technically demanding experiment which verified the Ahoronov-Bohm effect concerning the behaviour of charged particles in magnetic fields" |
| 1995 | Дэвид Шёнберг | "For his work on the electronic structure of solids, in particular by exploiting low temperature techniques, particularly the De Haas Van Alphen effect, defining the Fermi surface of many metals" |
| 1996 | Дэвид Букингем[en] | "For his contributions to chemical physics, in particular to long-range intermolecular forces, non-linear optics, problems related to the polarizability of the helium atom, the interpretation of NMR spectra, and the applications of ab initio computations" |
| 1997 | Эндрю Лэнг[en] | "For his fundamental work on X-ray diffraction physics and for his developments of the techniques of X-ray topography, in particular in studying defects in crystal structures" |
| 1998 | Реймонд Хайд[en] | "For his distinguished experimental and theoretical investigations of the hydrodynamics of rotating fluids and the application of such basic studies to the understanding of motions in the atmosphere and interiors of the major planets" |
| 1999 | Александр Боксенберг[en] | "For his landmark discoveries concerning the nature of active galactic nuclei, the physics of the intergalactic medium and of the interstellar gas in primordial galaxies. He is noted also for his exceptional contributions to the development of astronomical instrumentation including the Image Photon Counting System, a revolutionary electronic area detector for the detection of faint sources, which gave a major impetus to optical astronomy in the United Kingdom" |
| 2000 | Чинтамани Нагеса Рамачандра Рао | "For his contributions to the field of materials chemistry, in particular, in relation to studies of the electronic and magnetic properties of transition metal oxides and high temperature superconductors. His work has been an inspiration to a generation of Indian scientists" |
| 2001 | Джон Петика[en] | "For his contributions to the field of nanometre and atomic scale mechanics. He invented and developed the technique of nanoindentation thereby revolutionising the mechanical characterisation of ultra-small volumes of materials. This has had a major influence on those industries concerned with thin film and coating technologies" |
| 2002 | Александр Дальгарно | "For his contributions to the theory of atomic and molecular process, and in particular its application to astrophysics. His studies of energy depositions provide the key to understanding emissions from terrestrial aurorae, planetary atmospheres and comets" |
| 2003 | Питер Эдвардс[en] | "For his distinguished work as a solid state chemist. He has made seminal contributions to fields including superconductivity and the behaviour of metal nanoparticles, and has greatly advanced our understanding of the phenomenology of the metal-insulator transition" |
| 2004 | Джон Кларк | "For his outstanding research, leading the world in the invention, building and development of innovative new Superconducting QUantum Interference Devices (SQUID), in their theory and in their application to a plethora of fundamental problems and their investigative tools." |
| 2005 | Кейт Моффатт[en] | "For his contributions to the understanding of magnetohydrodynamics, especially to the mechanisms determining how magnetic fields can develop from a low background level to substantial amplitude." |
| 2006 | Майкл Келли[en] | "For his work in the fundamental physics of electron transport and the creation of practical electronic devices which can be deployed in advanced systems." |
| 2007 | Артур Экерт | "For his pioneering work on quantum cryptography and his many important contributions to the theory of quantum computation and other branches of quantum physics." |
| 2008 | Мишель Доэрти | "For innovative use of magnetic field data that led to discovery of an atmosphere around one of Saturn's moons and the way it revolutionised our view of the role of planetary moons in the Solar System." |
| 2009 | Не вручалась |
|
| 2010 | "For his revolutionary discovery of graphene, and elucidation of its remarkable properties" |
|
| 2011 | Мэтью Розински[en] | "For his highly influential discoveries in the synthetic chemistry of solid state electronic materials and novel microporous structures." |
| 2013 | Хеннин Сиррингаус[en] | "For his pioneering development of inkjet printing processes for organic semiconductor devices, and dramatic improvement of their functioning and efficiency." |
| 2015 | Джордж Эфстатиу[en] | "For many outstanding contributions to our understanding of the early Universe, in particular his pioneering computer simulations, observations of galaxy clustering and studies of the fluctuations in the cosmic microwave background." |
| 2017 | Peter Bruce[en] | "For distinguished work elucidating the fundamental chemistry underpinning energy storage." |
Примечания |
↑ 1234 Hughes Medal (англ.). Royal Society. Проверено 9 октября 2011. Архивировано 31 августа 2012 года.
Ссылки |
Медаль Хьюза (англ.) на сайте Лондонского королевского общества
ZISN7G8LEKg4EGYs7bkFTSo Q,ksKuMLGV2W0iZH9BQINVXi9tPb6,sCyYEAQYYF8om g15bPR cTd4q,DslD fGYh6wim lQ1,bEg